- Description
- Specifications
The Codonics SLS Safe Label System is based upon the SmartLabels technology licensed from Massachusetts General Hospital. The system was developed by anesthesiologists at Massachusetts General Hospital to prevent intravenous medication errors via barcode assisted medication labeling. At the 2008 ASA Annual Meeting, the system was awarded the Ellison C. Pierce Award from the Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation for best scientific exhibit in patient safety.
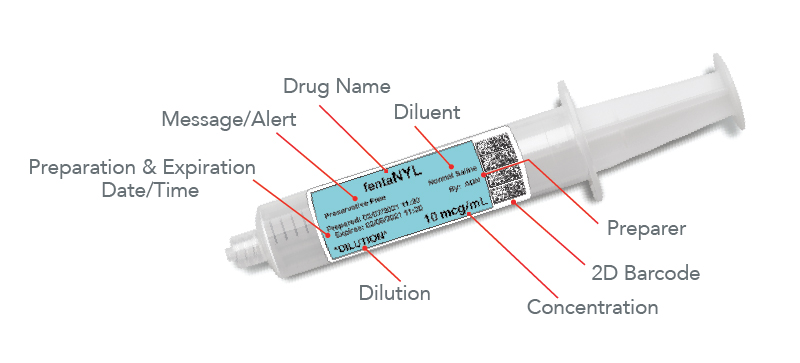
A 2009 study done by Massachusetts General Hospital with a Smart Label System evaluated compliance with The Joint Commission, ASA medication labeling requirements, patient safety, and clinician communication. The study evaluated five ORs where the labeling system was installed and compared them to manual syringe preparation by clinicians. The results showed 100% compliance was obtained using the automated system while less than half of the syringes prepared by the clinicians using traditional methods met TJC requirements. Clinicians were found to be very accepting of the system into their workflow, citing ease of use and utility of the safety features, such as audio and visual read-back of the data provided by the system. In addition to The Joint Commission labeling requirements, the system’s labels include date and time of preparation and expiration for all medications, are color-coded according to the ASA’s guidelines, and carry a 2D barcode of essential information that allows integration with an AIMS.
Improve Patient Safety
Multiple distractions, poor handwriting and look-alike/sound-alike drugs greatly contribute to the chance that drug containers could be confused or the wrong label is applied on a syringe.
- Complies with the APSF recommendation that every anesthetizing location should have a mechanism to identify medications before drawing them up (barcode reader).
- Includes visual and audible confirmations for each drug to help remove human error by incorporating machine-readable technology acting as an electronic double-check.
- Reduces the three most common drug errors made in the OR: Vial/ampoule swaps, mislabeling/illegible labeling and syringe swaps.
Possible Safety Features When Integrated with an Anesthesia information management system (AIMS)
- Identification of each syringe to be administered
- Warnings for expired syringes when scanned
- Warnings for patient allergies or adverse drug interactions
|
|
